Document Workflow Mappings
Version 25.3.9469
Version 25.3.9469
Document Workflow Mappings
An important component of the TPMC is configuring the mapping between the incoming or outgoing EDI document and the connector where the data is stored or sent to.
Incoming mappings rely on receiving EDI documents from a partner over an MFT protocol, translating them from EDI to XML using an EDI standard, then mapping them to a destination connector such as a database.
Outgoing mappings rely on pulling data as XML from a source connector (such as a database), mapping that data to an XML representation of an EDI standard, converting the XML to EDI, then sending the EDI document out to a partner over an MFT protocol.
Document workflows are defined in two ways.
- From the Partners tab, click the name of a partner, then choose the Workflows tab. See Select or Add Documents for instructions on how to add documents and launch a workflow.
- From the Documents tab, click the name of an existing document, or choose Add Document to create a new one. See Creating a Document from the Documents Tab for instructions on how to add a document and launch a workflow.
Add Document Workflow
Defining document workflows includes the following steps:
- Complete the Add Document Workflow screen.
- When you add a document from the Partners tab, click Add Workflow to launch the document workflow. In this case, the fields on the Add Document Workflow screen are prefilled. You can change the document name, but all other fields are fixed.
- When you add a document from the Documents tab, you must manually complete the fields on the Add Document Workflow screen.
- Select and configure the source or destination connector
- Configure the mapping. Mapping is applicable for all connectors except File, AMQP, and Apache Kafkawhich do not use mapping. See Document Workflow Without Mapping for more information.
Select and Configure the Source or Destination
When you create an incoming document, you must specify the destination connector where the data will be added. When you create an outgoing document, you must specify the source connector to pull the data from. The available connectors are the Arc Database and Other connectors, the File connector, the Workspace Send connector (for incoming documents only), and the Workspace Receive connector (for outgoing documents only).
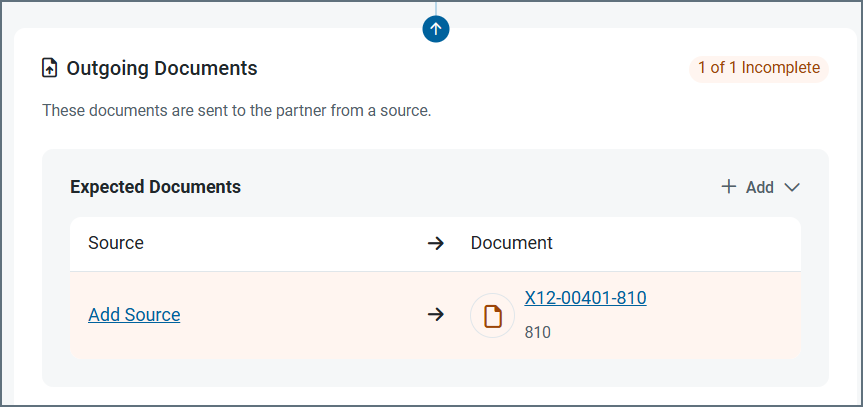
The following images show configuring a source for an outgoing document, but the same principles apply for incoming document destinations. In this example, the source is being defined from a partner’s Workflow tab, but you can achieve the same result from the Documents tab.
-
From the Workflow tab, click Add Source.
-
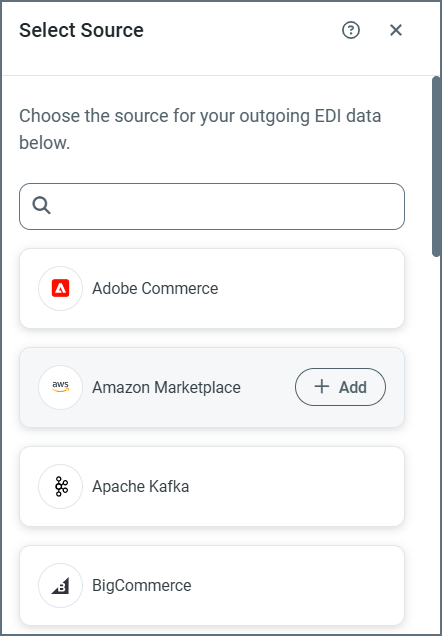
Highlight a connector in the Select Source list and click Add.
-
Use the plus sign to create a new Connection, or use the dropdown to select an existing one.
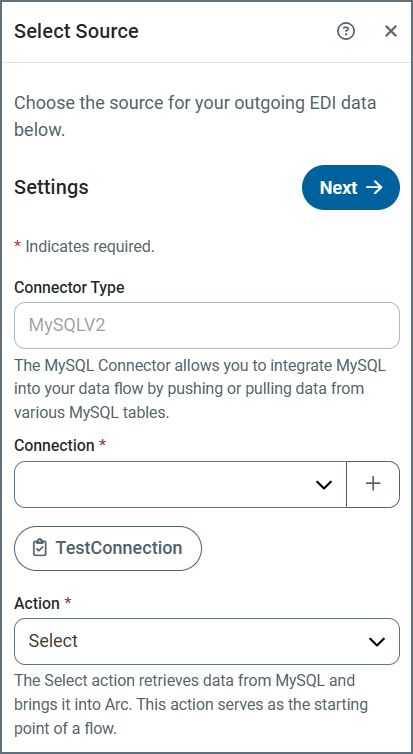
- When you add a new connection, complete the following fields in the Add Connection window:
- Name
- Server
- Port
- User
- Password
- AWS Access Key (optional)
- AWS Secret Key (optional)
- AWS Role ARN (optional)
- Click Test Connection.
- The only action available for an outgoing document is
Select, so when you have added and tested your connection, click Next. (The action for an incoming document isUpsert. See Actions for more information.)
This opens the Action connector configuration tab, where you complete the mappings. See Configure the Mapping for instructions on how to use this tab.
Notes:
- Use the other configuration tabs (such as Settings and Automation) to complete the connector configuration. For details on the configuration options, click the question mark help icon to open the connector documentation.
- If you need to modify the connection after the original setup, use the Connection field on the Settings tab.
Configure the Mapping
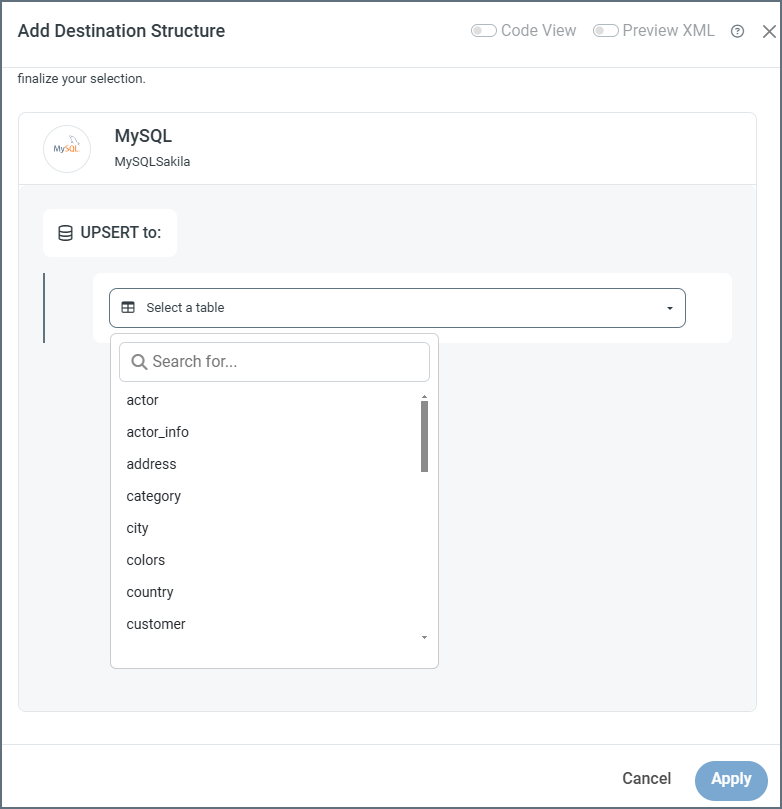
Once you have established the connection, you must select the table(s) that you need to map. If you’re creating an incoming document, click Add Destination Structure. If you’re creating an outgoing document, click Add Source Structure. This example shows adding a destination structure.
The following image of a completed mapping has been annotated to explain each element on the screen. Each number corresponds to a description below.
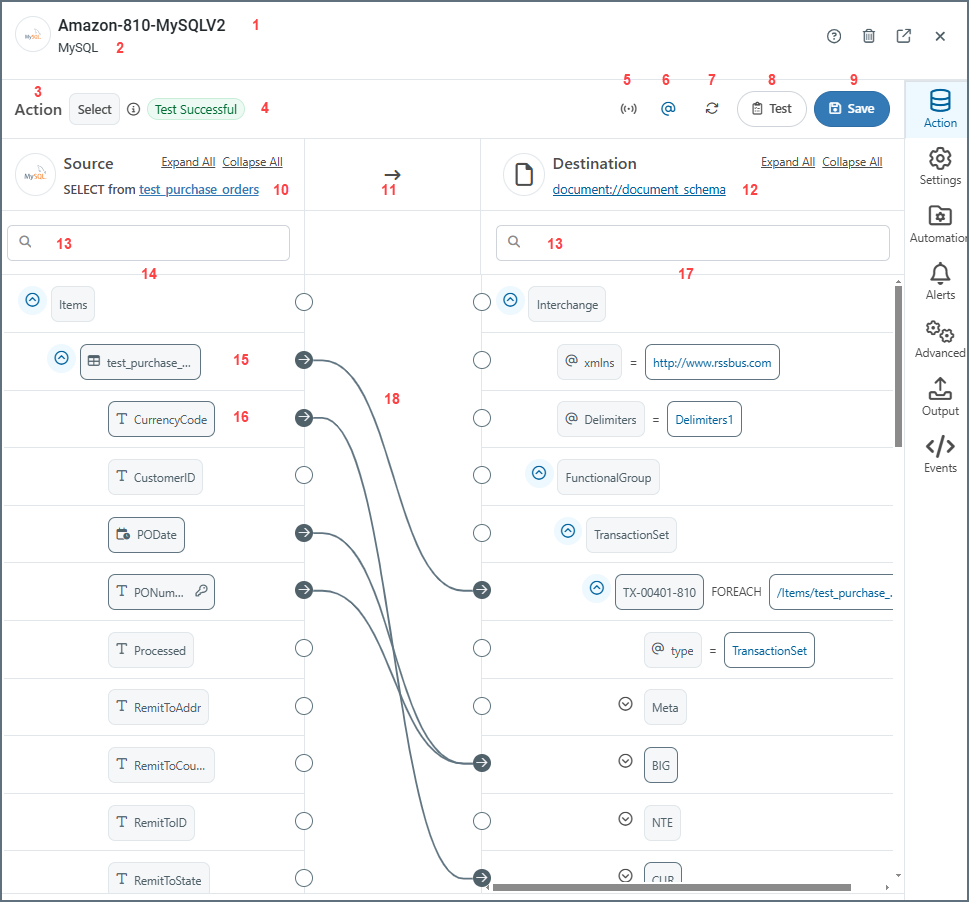
- The document or connector name.
- The connector type.
- The action for the document. Values are Upsert for incoming documents, and Select for outgoing documents.
- Test status of the mapping. Values are Test Successful, Tested with Errors or Not Tested.
- Toggles XML streaming on or off. When on, the mapping engine drops the Document Object Model (DOM) for the current iteration of the top-most
Foreachin the mapping after completing the loop. This can significantly improve performance for large XML documents. In situations where the mapping engine cannot resolve the mapping, it automatically toggles XML streaming off. - Toggles whether to show or hide the XML attributes.
- Refreshes the mapping.
- Opens the Test Mapping page. The test result is shown in #4. (See Testing Mappings for more information.)
- Saves the mapping.
- The target table in the configured data source.
- The direction of the mapping.
- The schema of the EDI document (an 810 invoice in this example).
- Search bars on the source and destination sides.
- Structure of the source table.
- The name of the table. This is also known as a table node.
- A column in the table. This is also known as a column node.
- The structure of the destination document.
- Completed mappings.
- Select a table from the dropdown.
- To add more tables to the mapping, click the link to the first table, then click the Add Child Table arrow and select the next table.
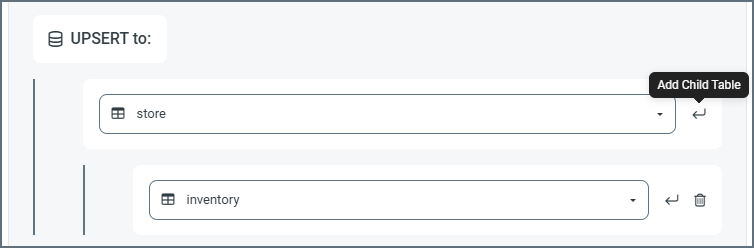
- Repeat these steps until you have added all the required tables. As you make changes, the mapping page displays the latest table structure.
The mapping page enables you to create the links between the EDI document and the source or destination connector. For incoming documents, the EDI document structure is in the left pane and the connector table structure is in the right pane. For outgoing documents it’s the reverse, as you can see in the annotated image below.
See Configure the Mapping in the Mapping documentation for detailed instructions on how to use the mapping editor.
Note: To edit a previously saved mapping, click EDI > Documents, then click the document name. In the Document Workflow section, click the link to the connector in the Document Destination (for incoming documents) or the Document Source (for outgoing documents).
Understanding Source and Destination
As mentioned previously, when you create an incoming document, you must specify the destination connector where the data will be sent. The EDI document structure is in the left pane and the connector table structure is in the right pane.
When you create an outgoing document, you must specify the source connector to pull the data from. Here, the connector table structure is in the left pane and the EDI document structure is in the right pane.
Arc provides a number of ways in which you can manipulate the information in the table and document structures. See Table Structure Nodes and Document Nodes for details.
To change the document schema, or to upload a template file that represents the source or destination XML structure, click the link to the document schema and choose Upload File. This is helpful if your partner provides you with a sample document of what they are expecting to send and/or receive. For example, if your partner provides you with a sample X12 850, you can convert it into XML by running it through an X12 connector in X12 to XML mode in a regular workspace. Then you can upload the output XML as a template file.
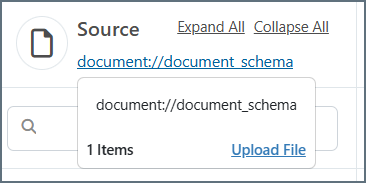
Browse to the template file, then click Upload Template File.
Actions
Two actions are available when you configure a connector:
- Upsert is the action for incoming documents. This action inserts or updates data into the target destination table. If a record already exists in the destination table, an update is performed on the existing data using the values provided from the input.
- Select is the action for outgoing documents. This action retrieves data from the target data source.
Table Structure Nodes
This topic describes the options available in the mapping pane that displays the source or destination table structure. There are two types of nodes in the structure: table nodes and column nodes. Table nodes represent the table itself and column nodes represent the columns in the table.
Table Nodes
Table nodes are indicated with a table icon. When you hover over a table node, you have two additional options:
-
Click the funnel icon to open the Add Mapping Conditions page which enables you to add filter conditions to the mapping. See Using the Condition Editor for more information. (Only available for incoming document mappings.)
-
Click the ellipses to open a list of options for that table node:
- Rename Table lets you change the name of the node.
- Remove Table removes the node.
- Table Settings opens an edit window that lets you select which columns to include in the mapping, and whether to apply filters. (Only available for outgoing document mappings.)
- Edit Columns opens an edit window that lets you select which columns to include in the mapping. (Only available for incoming document mappings.)
- Add opens a new list of nodes that you can create and use in your mappings. (Only available for incoming document mappings.) The options are:
- Add Header creates a header node that you can map a value to. The mapped value is not included in the output file but is added as a header on the mapping output message.
- Add Loop creates a loop node above the selected node and that node becomes nested within the loop node. See Mapping Loops for more information.
- Add Condition lets you add conditions to destination nodes so that data is only upserted to the destination if the condition is true. See Using the Condition Editor for details.
- Add Code Script opens the Add Script window where you can name the script node and supply custom ArcScript.
- Add Variable creates a variable node below the selected node. See Variables for more information.
Column Nodes
Column nodes represent columns in a table. Every column node has a type, which is the column’s datatype in the database. There are seven different datatypes, each one with its own symbol. Hover over a column to see its datatype, size, and whether it is nullable. The datatypes are:
- String
- Number
- Binary
- Boolean
- Date
- Time
- Date and Time
Hover over a column row and click the ellipses to open a list of options for that node:
- Rename Column lets you change the name of the node.
- Remove Column removes the node.
- Add opens a new list of nodes that you can create and use in your mappings. (Only available for incoming document mappings.) The options are:
- Add Header creates a header node that you can map a value to. The mapped value is not included in the output file but is added as a header on the mapping output message.
- Add Loop creates a loop node above the selected node and that node becomes nested within the loop node. See Mapping Loops for more information.
- Add Code Script opens the Add Script window where you can name the script node and supply custom ArcScript.
- Add Variable creates a variable node below the selected node. See Variables for more information.
- Add Tracking adds tracked headers to the mapping. When a node has tracking enabled, it displays a compass icon.
Document Nodes
Document nodes refer to the nodes on other side of the mapping: the non-database side. These nodes are not explicitly related to a data source (a table with columns) but rather represent the EDI data in an XML structure. These nodes are mapped to for outgoing documents and mapped from for incoming documents.
For outgoing documents (using the Select action), click the funnel icon to open the Add Mapping Conditions page which enables you to add filter conditions to the mapping. See Using the Condition Editor for more information. Click the ellipses to use the following options in the destination document:
- Rename Node lets you change the name of the node.
- Edit XPath lets you edit the node XPath (only on elements already mapped as
Foreach). - Delete Node lets you delete the node from the document.
- Add Node
- Add Sibling adds a node at the same level as the selected node.
- Add Attribute adds an attribute to the selected node.
- Add Child adds a node as a child of the selected node.
- Add Header creates a header node that you can map a value to. The mapped value is not included in the output file but is added as a header on the mapping output message.
- Add Loop creates a loop node above the selected node and that node becomes nested within the loop node. See Mapping Loops for more information.
- Add Condition opens the Condition Editor where you can add conditions so that data is only upserted to the destination if the condition is true.
- Add Code Script opens the Add Script window where you can name the script node and supply custom ArcScript.
- Add Variable creates a variable node below the selected node. See Variables for more information.
- Cut Node cuts the selected node from its current location.
- Copy Node copies the selected node.
- Paste as Child pastes the cut or copied node as a child of the selected node.
For incoming documents (using the Upsert action), click the ellipses in the source document structure to use the following options:
- Rename Node lets you change the name of the node.
- Delete Node lets you delete the node from the document.
- Add Node
- Add Sibling adds a node at the same level as the selected node.
- Add Attribute adds an attribute to the selected node.
- Add Child adds a node as a child of the selected node.
- Cut Node cuts the selected node from its current location.
- Copy Node copies the selected node.
- Paste as Child pastes the cut or copied node as a child of the selected node.
You can also use Edit Node to open the Edit Node Value page. See Using the Node Value Editor.
Test Mappings
Once you have configured the mapping, you should test it. Click the Test Mapping button at the top of the page. The following image shows testing an incoming document.
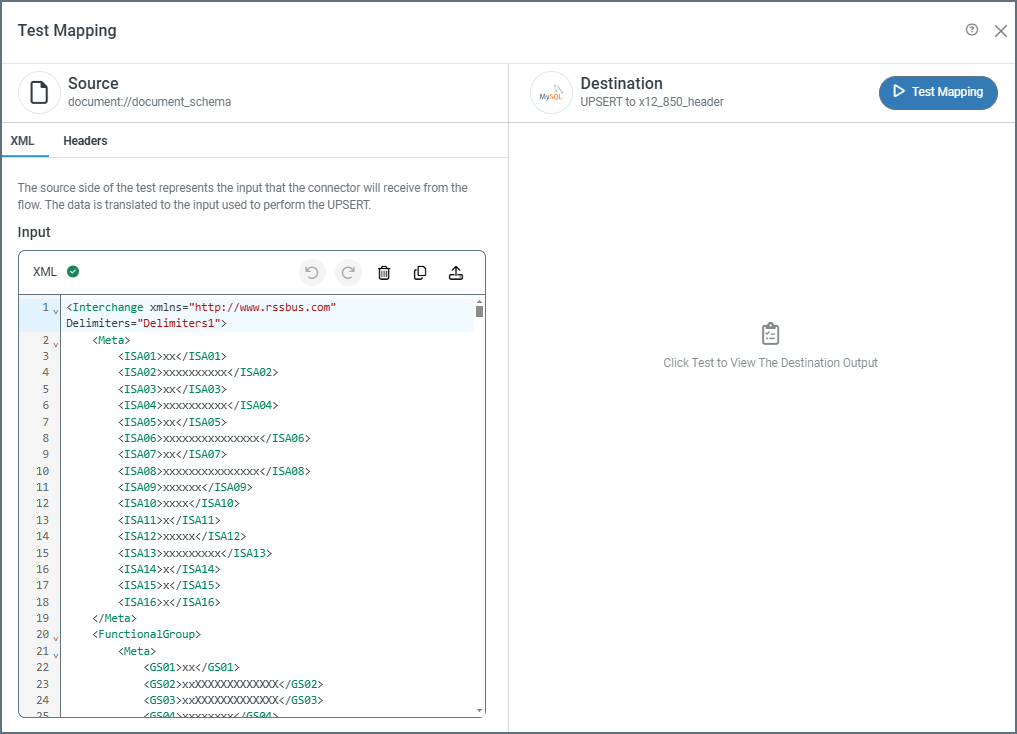
The source side of the test page has two tabs: XML and Headers (the Headers tab is only available on incoming documents). The source is populated with the XML representation of the document or table structure to test, but you can edit it as necessary. For incoming documents, click the Headers tab to add any headers you want to use in the mapping (see Tracked Headers for more information). When you are ready, click Test Mapping.
Test result indicators appear on the partner Workflow page and on the mapping itself. The values on the mapping are Test Successful, Tested with Errors or Not Tested. The Workflow page shows a check for successful tests, a brown exclamation mark for untested mappings, and a red exclamation for tests with errors. Hover over the icons for details about the errors.
Note: When you test incoming documents, you are testing with live data. When you click Test Mapping, Arc tries to perform the upsert after it tests the mapping.
Using Filters
If you need to filter the data that the connector selects in a source table structure, click the ellipses and choose Table Settings, then click the Filters tab. The Edit <TableName> Settings window opens, where you can define individual filters and filter groups.
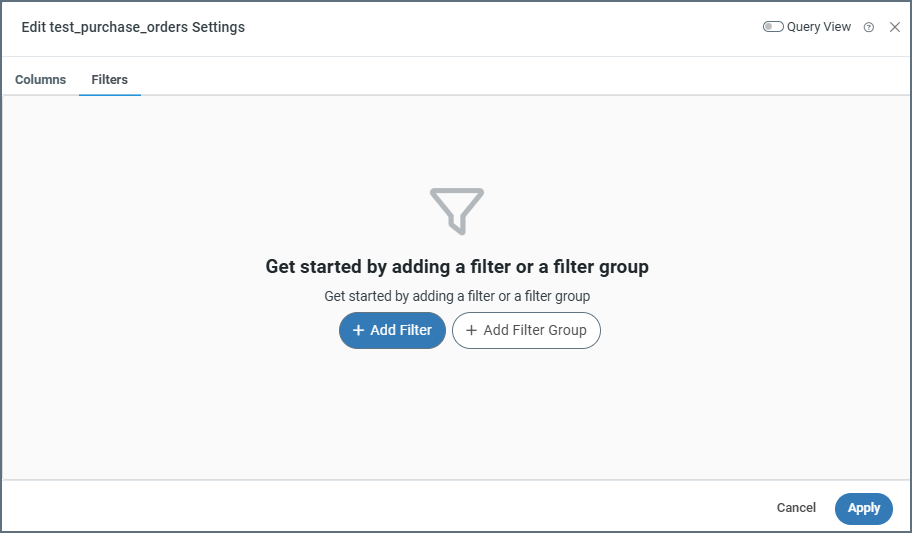
Creating a Filter Rule
To create a filter, follow these steps:
- Click Add Filter.
- In the drop-down list for the new rule, choose the column that you want to filter.
- Choose the filtering condition. The available filtering conditions depend on the data type for the column you select.
- If your filtering condition requires a value, enter that value in the blank value field. If your filtering condition does not require a value (for example, if you choose Is Null), the value field disappears.
For example, you could create a filter on a column named Author that only selects values that contain Smith. In this example, the column is Author, the condition is Contains, and the value is Smith.
Filter Groups
You can apply multiple filters to your table by clicking Add Filter. Filters are separated by groups, and all filters belong to the same group by default. You can create multiple groups to separate filters by clicking Add Group.
Each filter in a group interacts with the others based on the options you select at the top of the group:
- Use the NOT toggle to invert the filter conditions. For example, in the Author filter example above, enabling the NOT toggle instructs the connector to select Author values that do not contain Smith.
- Select AND or OR to determine the group logic for multiple filters.
- If you select AND, every filter in the group must be true for the filter conditions to be met.
- If you select OR, at least one filter in the group must be true for the filter conditions to be met. Multiple filter can be met, and the results are the same as if only one were met.
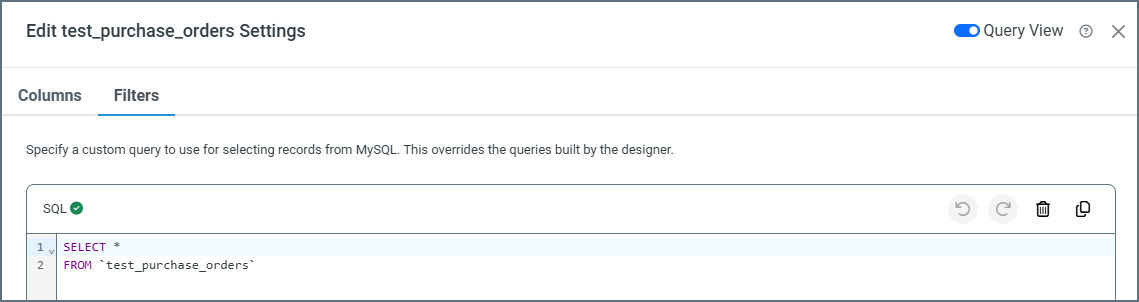
Using Query View
Toggle on Query View to write a custom SQL query that selects data from your data source. This overrides any queries created in the designer.