Configure an OFTP Connection
Version 25.3.9469
Version 25.3.9469
Configure an OFTP Connection
Overview
CData Arc supports establishing an Odette FTP (OFTP) connection with a trading partner in a simple two-step process. First the OFTP profile is configured with local OFTP details (identifier, private certificates, and so on). Then an OFTP connector is configured on the Flows page with the OFTP details for a specific trading partner.
The OFTP protocol supports message routing and clearing-house servers, which can cause confusion when establishing a new connection. See SSID and SFID to learn more about message routing, SSIDs, SFIDs, and how these concepts are captured in Arc.
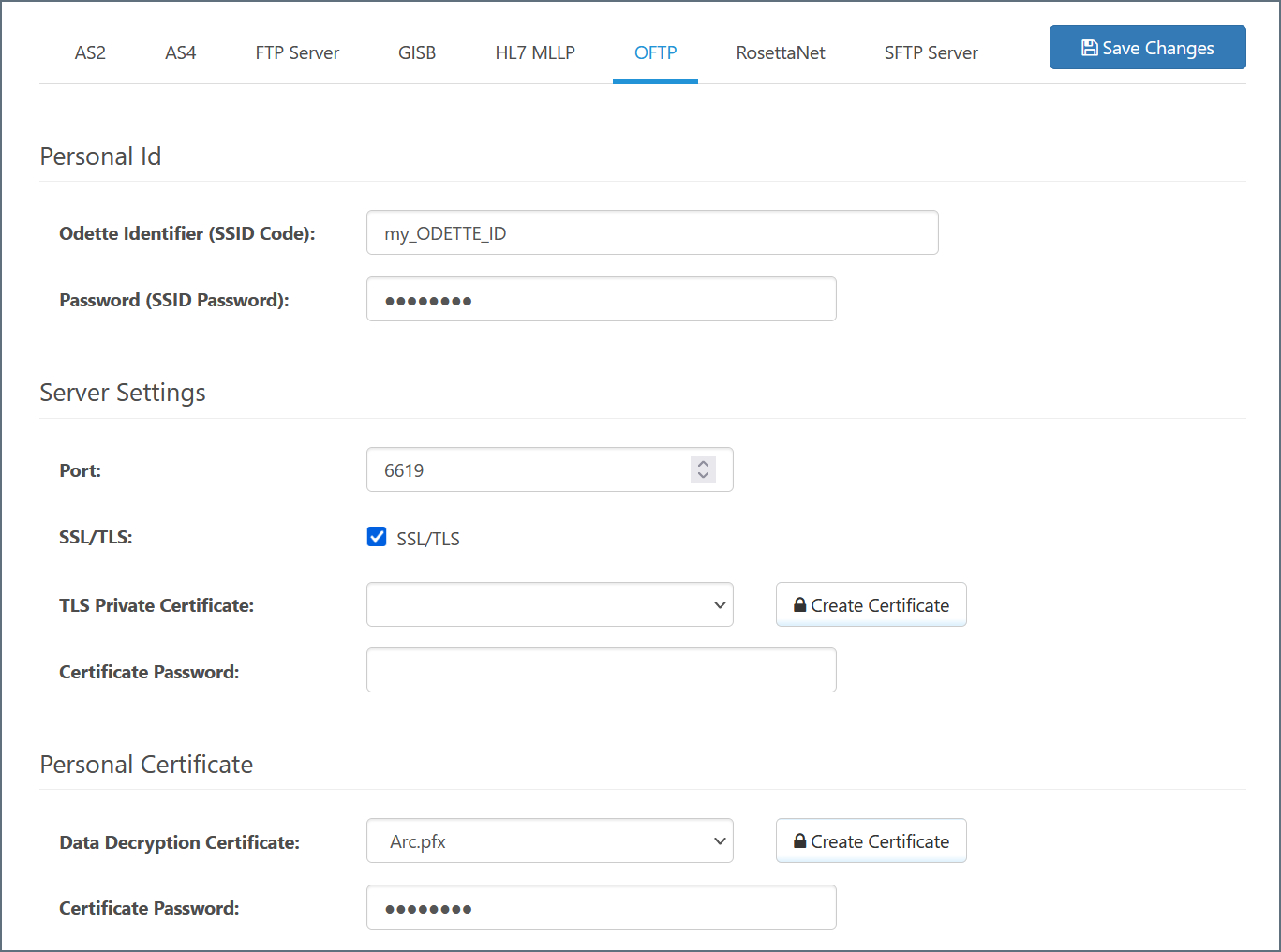
OFTP Profile Configuration
The Profiles page contains an OFTP section where local OFTP details are configured. The primary configuration details are:
- Odette Identifier (the value provided by Odette that identifies you as an OFTP entity)
- Server Settings (parameters related to ports and TLS settings)
- Password (the password associated with your identifier; this is an arbitrary value that you provide to trading partners)
- Private Certificate (the certificate that is used to decrypt incoming messages and sign outgoing messages)
Click Profiles on the navbar to configure the OFTP profile settings, as described below.
Odette Identifier
Your Odette identifier is assigned by Odette and identifies you as an OFTP entity. It is included in outgoing OFTP messages and identifies you as the sender. Additionally, incoming OFTP messages must be addressed to this identifier to be accepted by the application.
Note: OFTP uses two different values to identify the recipient of a message: SSID and SFID. Sometimes these are the same value, and sometimes they are not, which can cause confusion. SSIDs and SFIDs (and how they relate to the settings in Arc) are explained in detail in SSID and SFID.
Password
Unlike the identifier, the password is an arbitrary value that you must agree upon with your trading partners (in other words, you can make this value up as long as you send it to your partners and they agree with what the password should be).
The password value must be known by both the sender and receiver to successfully send and receive OFTP messages.
Server Settings
The Server Settings section of the profile defines the core parameters of the OFTP server that will listen for inbound messages. Port specifies the port on which inbound OFTP connections are accepted, and the Use SSL/TLS setting determines whether inbound connections must be encrypted with TLS/SSL security. If TLS is enabled, you must set up a TLS/SSL certificate and password to identify the server. This is not the same as the Personal Certificate settings described below. Those are used for decrypting OFTP messages after they have been received over the connection channel.
Personal Certificate
Your personal certificate is used for digital cryptography (decryption and digital signatures). The Data Decryption Certificate is a certificate with a private key that is paired with your public encryption key. When a trading partner uses the public key of your Data Decryption Certificate to secure an OFTP message, it ensures that only you can decrypt the message (with the paired private key).
Arc supports private certificates in PKCS#12 format (.pfx or .p12 files), and PEM-encoded public key certificates (.cer files).
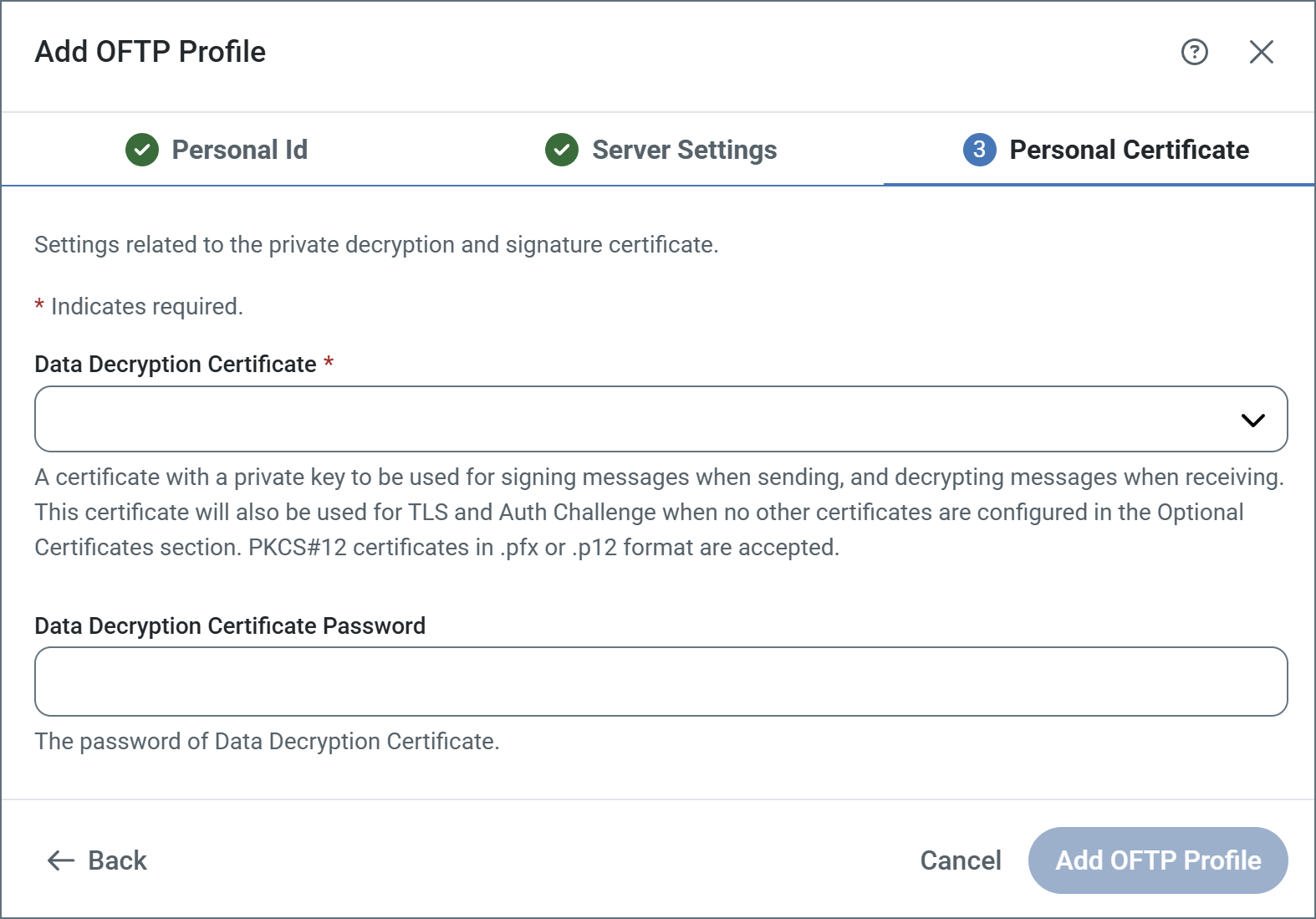
Creating a New Certificate Pair
If you do not already have a private and public key pair to use for OFTP security, Arc supports creating a self-signed certificate. Self-signed certificates are common in the OFTP space, but some partners might require purchasing a certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
To create a new certificate pair, choose Create Certificate in the Data Decryption Certificate dropdown:
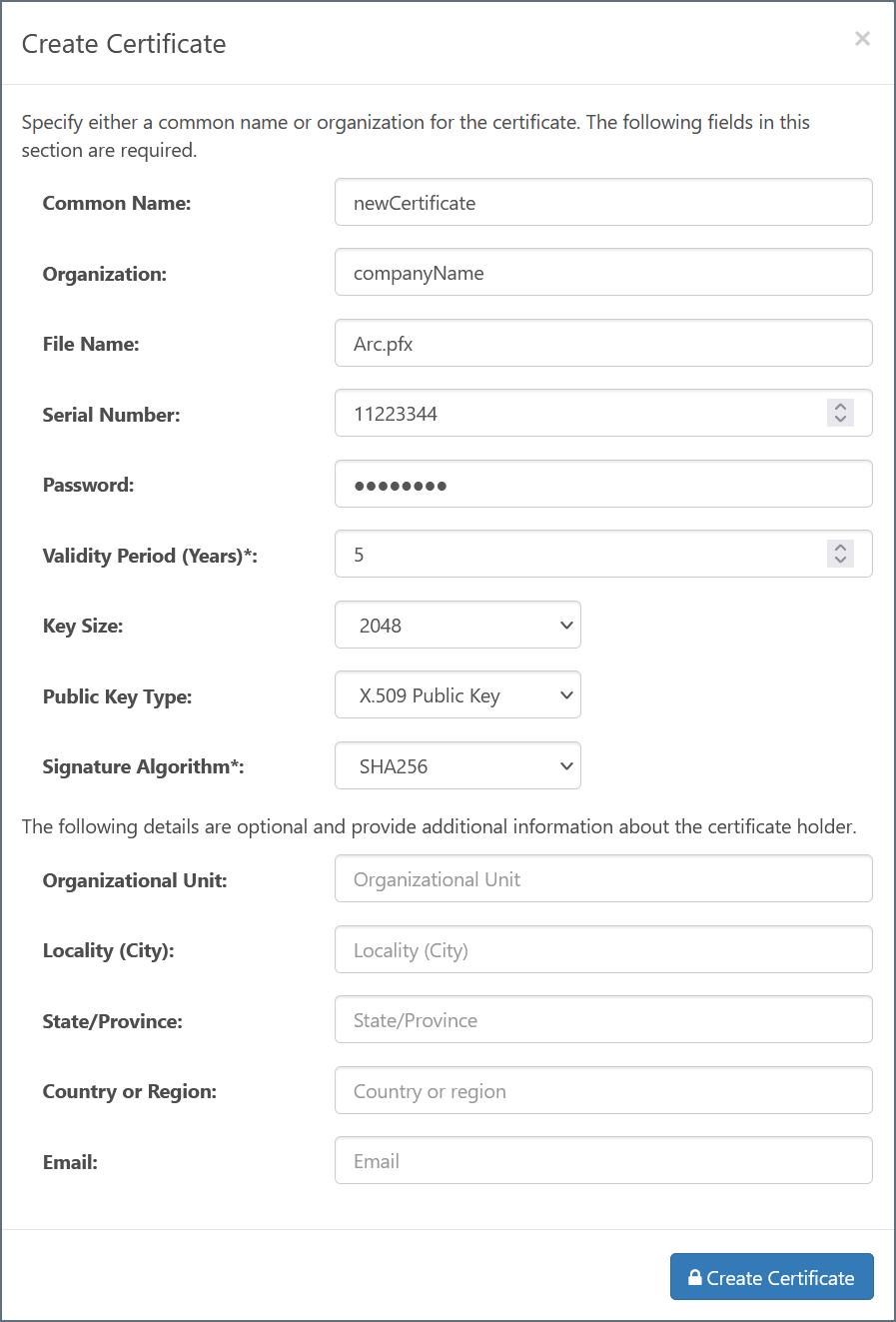
The following fields are required:
- Common Name: The hostname of the server using the certificate. It is used in conjunction with the serial number to identify the certificate.
- File Name: The name of the certificate file, with a
.pfxextension. The corresponding public key certificate is given the same name with a.cerextension. - Serial Number: A unique serial number that is used in conjunction with the common name to identify the certificate.
- Password: The password required to access the private key.
- Validity Period: Determines the expiration date of the certificate.
- Key Size: Whether to create a 512, 1024, 2048, or 4096-bit key.
- Public Key Type: Whether to create an X.509, OpenSSH, or SSH2 public key.
- Signature Algorithm: The algorithm to use when applying a digital signature to the certificate to verify its authenticity.
The remaining fields are optional. but you can use them to add further context and metadata to the certificate.
Once created, the certificate files are placed in the application data directory. Certificate files in this directory are included in the dropdown lists of any certificate-type settings in the application.
OFTP Connector Configuration
After the OFTP profile is configured, navigate to the Flows page and create an instance of the OFTP connector.
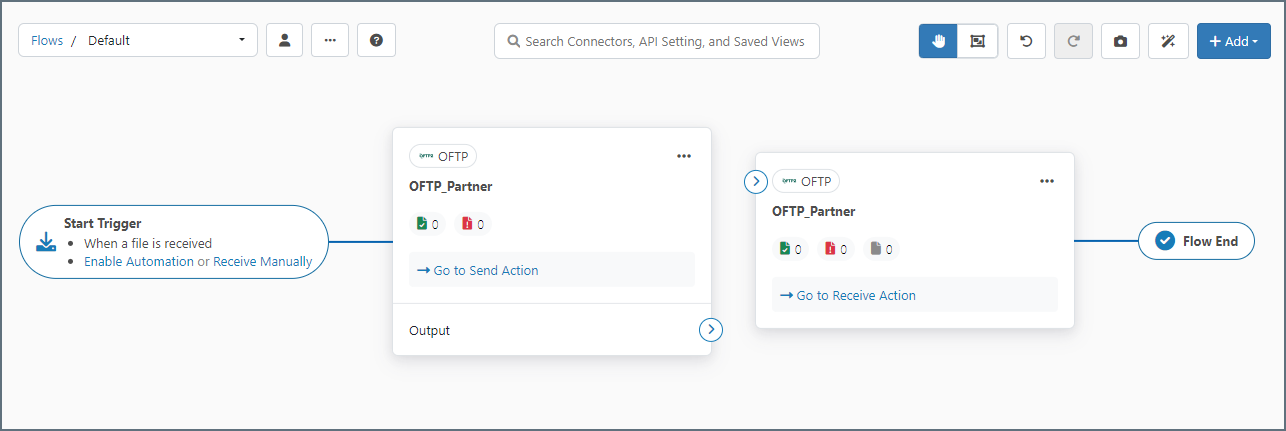
Typically, each OFTP connector is configured with the OFTP details for a single trading partner. However, sometimes a partner can require two OFTP connectors. Details on when two connectors are required, and how the configuration differs between the two, are explained in SSID and SFID.
Required Configuration Settings
OFTP configuration details must be provided by the trading partner. At a minimum, the details that the trading partner must provide include:
- Odette identifier
- Password
- Hostname or IP address where outgoing OFTP messages should be sent
- Port where the remote host is listening
- Public certificate or key for encryption
Configure these values under the Host Configuration and Trading Partner Certificates sections of the OFTP connector Settings tab:
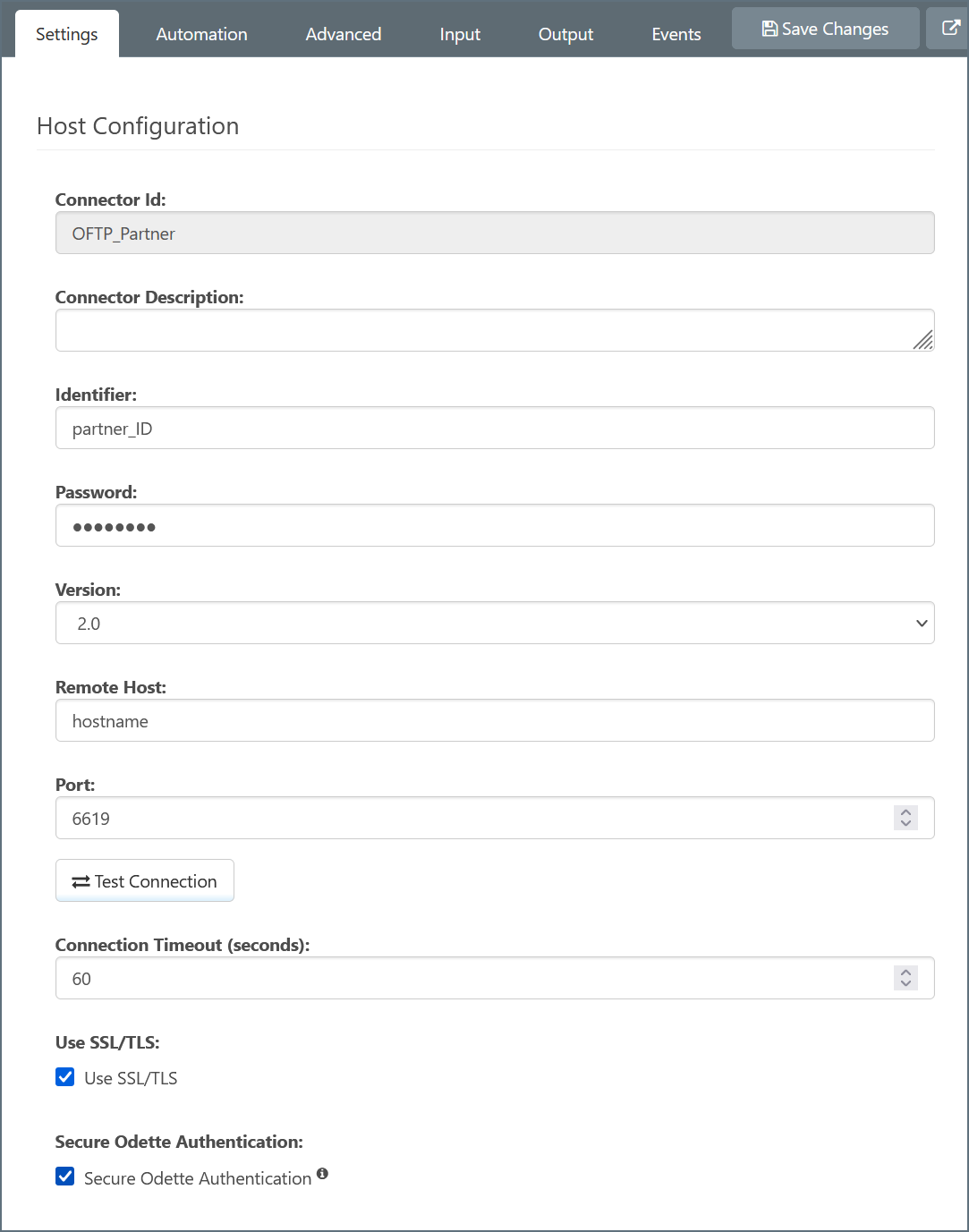
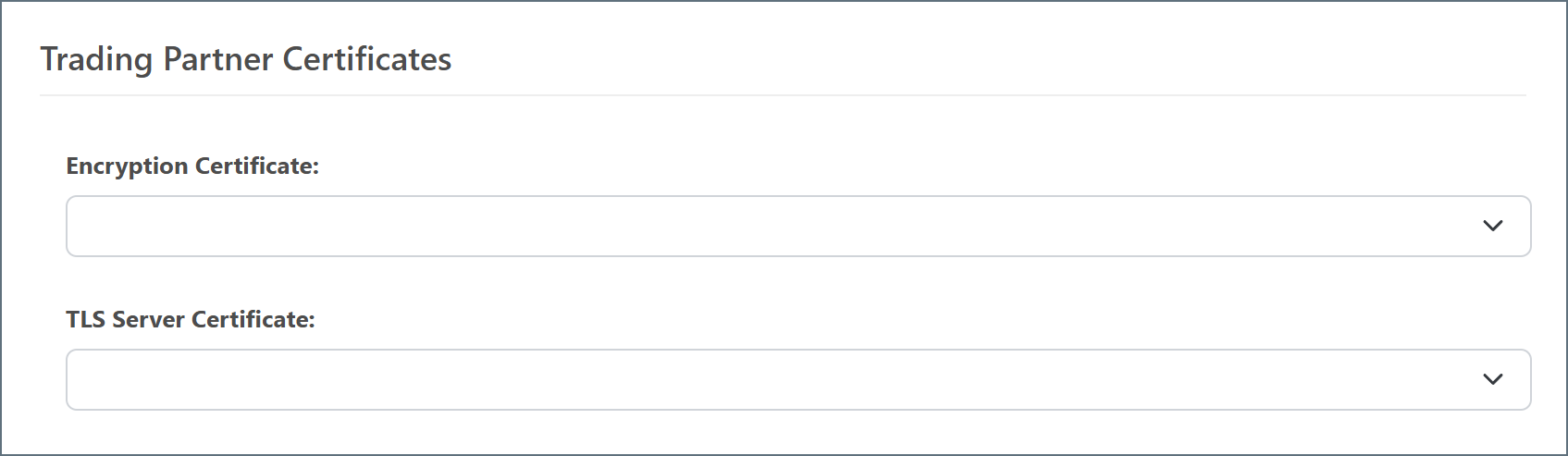
Additional Configuration Settings
Partners can include additional requirements, including:
- SSL/TLS and an additional TLS Server Certificate: SSL/TLS is configured on the Settings tab, and the additional certificate is configured on the Advanced tab. If this is not specified, assume it is not required.
- Secure Odette Authentication: Configured on the Settings tab. If this is not specified, assume it is required.
- Virtual File Format: Configured on the Settings tab. If this is not specified, assume the file format is unstructured.
Logging
Enabling server-side logging can be helpful for debugging OFTP connection issues. When debugging, CData recommends you set the Log Level on the connector’s Advanced tab to Debug. Logs can be configured to rotate (in other words, compressed and moved to an archive location) or be deleted according to your chosen interval.
Note: When you are not actively debugging, keep Log Level set to Info.
Testing the OFTP Connection
Once the configuration for a trading partner is complete, you can test the outgoing connection by generating test documents. Navigate to the OFTP connector’s Input tab and choose More > Create Test Files.
Unless Send Automation is disabled on the Automation tab, the connector automatically attempts to process these test files. Any errors that occur when sending the test files to the configured partner are reported on the Input tab, including a log file with context and details on the error. To further diagnose connection issues, use the Log Level and Log Messages options on the Advanced tab.
Successfully processed files are shown with a green Sent status on the Input tab. Successfully sending test files establishes that the OFTP configuration is correct.
Providing OFTP Details to Trading Partners
In the same way that trading partners must give you OFTP configuration details in order to configure an OFTP connector for that partner, you must provide OFTP configuration details to your partners.
At a minimum, you must provide your partner with:
- Your Odette identifier
- Your password
- Your public key or encryption certificate
- Your receiving hostname or IP address and port
Sending OFTP Messages
Once an OFTP connector has successfully established an outgoing OFTP connection, files can be securely and reliably sent to your trading partner.
Input Tab
Files placed in the OFTP connector Input tab are scheduled to be sent by the connector.
If Send Automation is enabled on the Automation tab (it is enabled by default), the connector automatically polls this folder for files to process. Alternatively, you can manually send files from the Input tab. Click the checkbox to the left of the target file(s) and click the Send button.
You can also use the Input tab to upload files into the Send folder.
Sending as Part of a Flow
In most workflows, files are processed by other Arc connectors before they are sent out by the OFTP connector. When another connector is connected to the OFTP connector in a flow, files are automatically passed into the OFTP connector’s Send folder.
Receiving Receipts
The connector automatically waits for OFTP receipts if Request Signed Receipts is enabled on the Settings tab. If the receipt contains a negative response (for example, the partner has rejected the exchange for some reason), the connector reports an error instead of a successful send.
Receiving OFTP Messages
When an OFTP message arrives on the Arc OFTP server, the application attempts to route the message to a specific OFTP connector. Arc uses the Odette identifiers in the message headers to route the incoming file to the OFTP connector configured for the partner that sent the message.
If the application cannot find an OFTP connector configured for the incoming message (based on OFTP identifiers), an error is logged on the Application log tab and the file is not received.
Output Tab
When the file received over OFTP is routed to a specific OFTP connector (based on configured Odette identifiers), the file arrives in the Output tab for the connector.
If the OFTP connector is connected to other connectors in the flow, files do not stay in the Receive folder and are instead passed along to the next connector in the flow.
If the OFTP connector is not connected to another connector in the flow, the files received by the OFTP connector remain in the Receive folder. These files can be viewed on the Output tab of the connector.
Sending Receipts
If the incoming OFTP message requests a receipt, the OFTP connector automatically generates and sends the receipt. If an error occurs while receiving the OFTP message, this error is logged in Arc and included in the receipt returned to the trading partner.
The settings required for sending receipts are included in the incoming OFTP message and do not need to be explicitly configured in the OFTP connector.
SSID and SFID
This section provides a conceptual overview of SSID and SFID values, message routing, and how the Arc settings are used to define and control the connection behavior. A conceptual understanding of message routing in OFTP helps clarify the role of the SSID and SFID values in establishing a connection and transferring files.
Message Routing
When an OFTP client sends a file to an OFTP server, the client can request that the OFTP server forward the file to another OFTP entity or server. This process of sending a file to serverA with the expectation that it is routed to serverB is what is meant by message routing.
A common use case for message routing is to have a single server act as a gateway, or clearing house, for multiple OFTP endpoints. For example, imagine a company with three branches, each of which needs to receive unique OFTP messages. A single OFTP server can act as a clearing house for the entire company, receiving OFTP messages from outside and routing them to the appropriate internal OFTP endpoint (with an OFTP server dedicated to each branch).
However, OFTP connections do not need to use message routing; a direct connection can be established from one endpoint to the other and messages passed without any intermediary steps.
SSID
When an OFTP client connects to an OFTP server, it informs the server of its identity by sending the server its Odette identifier and associated password. If the server recognizes this Id and should allow the connection, the server sends back its own Odette ddentifier and password. Only when both sides recognize the other (by Id) does the connection succeed.
These Id values are exchanged using SSID commands, which stands for Start Session ID. Think of an SSID value as the Id used to confirm the identity of the remote side when establishing an OFTP session (a connection).
SFID
An SFID, which stands for Start File ID, is also an Odette identifier value, but it is used in a different way from the SSID. While the SSID is used to initiate a session (connection) with an OFTP server, the SFID is used to identify the ultimate recipient of a file. When a client sends a file over OFTP, it includes an SFID value to let the remote side know whether the file should be routed to another OFTP entity.
This means that the SFID value can be the same as the SSID of the server, if the file is meant to stay at the target server. It can also be different, if the client is connecting to a clearing house or gateway OFTP server, and that server needs to route the file to the end recipient.
Using SSID and SFID Values in CData Arc
Configuring the correct SSID and SFID values in Arc depend on whether your OFTP trading partner requires message routing or not. When a trading partner provides two different identifier values for the SSID and SFID, this indicates that the partner requires message routing.
Configuration When Routing Messages
If your partner requires message routing, you need to configure two separate OFTP connectors. One connector (call it connectorA) is configured with the connection details for the clearing house server (the server in the middle), while the other connector (connectorB) is configured with the connection details for the end recipient server.
The Odette Identifier field in connectorA holds your partner’s SSID value, or the value used to identify the clearing house server. The Odette Identifier field in connectorB holds your partner’s SFID value, or the value used to identify the end recipient server. In addition, connectorB must have the Routing Partner field on the Settings tab set to connectorA.
Once this setup is configured, files that are sent to the partner are uploaded or input to connectorB. This connector uses connectorA to connect to the clearing house server (as a result of setting Routing Partner), and routes the file with the SFID value from the Odette Identifier field in connectorB to the correct target destination.
Configuration When Transferring Files Directly
If your partner does not require message routing, they should provide a single SSID or SFID value to identify their OFTP server. You only need to configure one OFTP connector (in contrast to the two connectors required when message routing is involved), and the Odette Identifier field in the connector should be set to the SSID or SFID value provided by the partner.