TRADACOMS Connector
Version 24.3.9159
Version 24.3.9159
TRADACOMS Connector
TRADACOMS connectors support generating TRADACOMS documents from XML and converting TRADACOMS documents into XML.
Overview
When receiving TRADACOMS documents, TRADACOMS connectors validate interchange headers and convert the TRADACOMS document into XML. This is useful as a staging step, because XML is the primary format that CData Arc uses to manipulate data in a flow. The TRADACOMS connector automatically reads the input file to determine the appropriate schema, then parses the document according to this schema.
When generating TRADACOMS documents, TRADACOMS connectors convert XML into TRADACOMS document syntax and apply the appropriate interchange headers. This is useful as the final step for creating an TRADACOMS document, after the XML data has been fetched and transformed elsewhere in the flow.
Connector Configuration
This section contains all of the configurable connector properties.
Settings Tab
Translation Configuration
Settings related to the core operation of the connector.
- Connector Id The static, unique identifier for the connector.
- Connector Type Displays the connector name and a description of what it does.
- Connector Description An optional field to provide a free-form description of the connector and its role in the flow.
- Translation Type Whether the connector should convert TRADACOMS documents into XML, or XML data into TRADACOMS documents.
Transmission Settings
Settings related to the transmission headers of TRADACOMS documents. When generating documents, these settings are applied as interchange headers in the resulting document. When parsing documents, the interchange settings are used to validate the incoming document.
- Syntax Identifier (STDS Identifier) Identifies the syntax rules used in the TRADACOMS document.
- Sender Code (FROM Code) Identifies the party sending the TRADACOMS document. When generating TRADACOMS from XML, this should be your code.
- Sender Name (FROM Name) The name of the party sending the TRADACOMS document (optional). When generating TRADACOMS from XML, this should be your name.
- Recipient Code (UNTO Code) Identifies the party receiving the TRADACOMS document. When converting TRADACOMS into XML, this should be your code.
- Recipient Name (UNTO Name) The name of the party receiving the TRADACOMS document (optional). When converting TRADACOMS into XML, this should be your name.
- Sender Reference (SNRF) The Id used to reference the sender of the TRADACOMS document.
- Receiver Reference (RCRF) The Id used to reference the recipient of the TRADACOMS document.
- Application Reference (APRF) The Id used to reference the TRADACOMS application for this document exchange.
- Transmission Priority Code (PRCD) The code representing the priority of the TRADACOMS transmission.
Automation Tab
Automation Settings
Settings related to the automatic processing of files by the connector.
- Send A toggle that instructs the connector to automatically send files when they are ready.
- Resend Interval The interval the connector waits before resending a file that received a negative ACK. For example, if a trading partner receives the file but something is wrong with it and they send back a negative ACK, this setting specifies how long to wait before sending the file again.
- Max Attempts (async) The maximum number of times the connector processes the input file when a functional ACK is requested. Success is based on the return of a functional ACK within the Resend Interval. If a successful functional ACK is not returned, the connector resends the file until Max Attempts is reached. If this is set to 0, the connector resends the file indefinitely.
Performance
Settings related to the allocation of resources to the connector.
- Max Workers The maximum number of worker threads consumed from the threadpool to process files on this connector. If set, this overrides the default setting on the Settings > Automation page.
- Max Files The maximum number of files sent by each thread assigned to the connector. If set, this overrides the default setting on the Settings > Automation page.
Alerts Tab
Settings related to configuring alerts and Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
Connector Email Settings
Before you can execute SLAs, you need to set up email alerts for notifications. Clicking Configure Alerts opens a new browser window to the Settings page where you can set up system-wide alerts. See Alerts for more information.
Service Level Agreement (SLA) Settings
SLAs enable you to configure the volume you expect connectors in your flow to send or receive, and to set the time frame in which you expect that volume to be met. CData Arc sends emails to warn the user when an SLA is not met, and marks the SLA as At Risk, which means that if the SLA is not met soon, it will be marked as Violated. This gives the user an opportunity to step in and determine the reasons the SLA is not being met, and to take appropriate actions. If the SLA is still not met at the end of the at-risk time period, the SLA is marked as violated, and the user is notified again.
To define an SLA, click Add Expected Volume Criteria.
- If your connector has separate send and receive actions, use the radio buttons to specify which direction the SLA pertains to.
- Set Expect at least to the minimum number of transactions (the volume) you expect to be processed, then use the Every fields to specify the time frame.
- By default, the SLA is in effect every day. To change that, uncheck Everyday then check the boxes for the days of the week you want.
- Use And set status to ‘At Risk’ to indicate when the SLA should be marked as at risk.
- By default, notifications are not sent until an SLA is in violation. To change that, check Send an ‘At Risk’ notification.
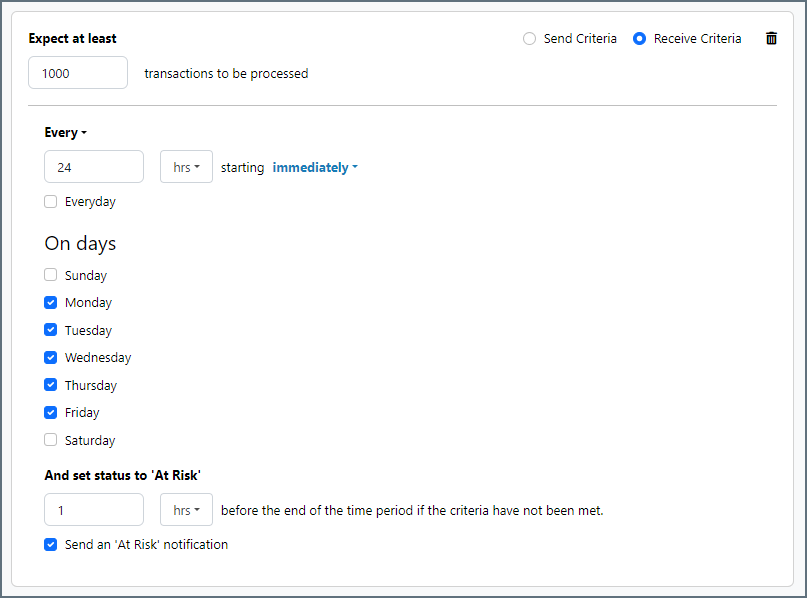
The following example shows an SLA configured for a connector that expects to receive 1000 files every day Monday-Friday. An at-risk notification is sent 1 hour before the end of the time period if the 1000 files have not been received.
Advanced Tab
EDI Delimiters
Settings that specify which characters separate elements, segments, and so on.
- Data Element Separator The character that separates individual data elements in the document.
- Component Element Separator The character that separates elements within a composite data structure in the document.
- Segment Terminator The character that indicates the end of a segment in the document.
- Release Char The character that releases (escapes) the next character, overriding its usual meaning. This allows reserved characters to appear as data within documents, as long as they are preceded by the Release Char.
- Suffix Appended to the Segment Terminator to distinguish segments.
Advanced Settings
Settings not included in the previous categories.
- Batch Transactions An interchange can contain multiple transactions. When this is not checked, the connector creates a separate output file for each transaction in the interchange. When checked, the connector groups all transactions into a single output file. Only applicable when the Translation Type is TRADACOM to XML.
- Encoding Specifies the character encoding (such as ASCII or UTF-8).
- Expand Qualifier Values When checked, XML elements containing an EDI qualifier include child elements containing the qualifier code and value. Only applicable when the Translation Type is TRADACOM to XML. For example:
<N101>
<Code>ST</Code>
<Value>Ship To</Value>
</N101> - Generate Description As When translating TRADACOM into XML, descriptions of the TRADACOM segments and elements can be provided as context for the TRADACOM data. Use this dropdown to choose whether to add this context as an XML comment or as XML attributes.
- Local File Scheme A scheme for assigning filenames to messages that are output by the connector. You can use macros in your filenames dynamically to include information such as identifiers and timestamps. For more information, see Macros.
- Nest Loops When checked, the connector detects EDI structures that have hierarchical relationships embedded in the EDI data, and generates XML with these hierarchical relationships represented as parent-child relationships.
- Processing Delay The amount of time (in seconds) by which the processing of files placed in the Input folder is delayed. This is a legacy setting. Best practice is to use a File connector to manage local file systems instead of this setting.
- Strict Schema Validation Whether the connector should Ignore, Warn, or Fail when the following are detected: repeat counts above the allowed number, missing required elements or segments, invalid qualifier and code values, disallowed element lengths, and invalid element values. Choosing Disable turns off the schema validation checks.
- Track Transaction Types Whether to add transaction types as tracked headers to processed messages. These headers are required when running Reports.
- Validate Identifiers Check this to ensure that the identifiers in the translated document match the identifiers in the connector’s configuration.
- Upload Schema Use this to upload a schema and install it in the connector’s Schema folder. If a schema already exists, you are asked if you want to overwrite it.
- Reset State EDI connectors keep track of control numbers that have been used and increment that number to ensure that future runs do not duplicate data. Use this button to reset the counter to its initial state without changing any of the configured settings.
Message
- Save to Sent Folder Check this to copy files processed by the connector to the Sent folder for the connector.
- Sent Folder Scheme Instructs the connector to group messages in the Sent folder according to the selected interval. For example, the Weekly option instructs the connector to create a new subfolder each week and store all messages for the week in that folder. The blank setting tells the connector to save all messages directly in the Sent folder. For connectors that process many messages, using subfolders helps keep messsages organized and improves performance.
Logging
- Log Level The verbosity of logs generated by the connector. When you request support, set this to Debug.
- Log Subfolder Scheme Instructs the connector to group files in the Logs folder according to the selected interval. For example, the Weekly option instructs the connector to create a new subfolder each week and store all logs for the week in that folder. The blank setting tells the connector to save all logs directly in the Logs folder. For connectors that process many transactions, using subfolders helps keep logs organized and improves performance.
- Log Messages Check this to have the log entry for a processed file include a copy of the file itself. If you disable this, you might not be able to download a copy of the file from the Input or Output tabs.
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous settings are for specific use cases.
- Other Settings Enables you to configure hidden connector settings in a semicolon-separated list (for example,
setting1=value1;setting2=value2). Normal connector use cases and functionality should not require the use of these settings.
TRADACOMS to XML
When generating XML, set the Translation Type to TRADACOMS to XML. TRADACOMS files placed in the Input tab are processed by the connector. The connector validates TRADACOMS message headers against the configured Transmission Settings. After validating the transmission, the TRADACOMS segments are converted into XML according to the schema specified in the message. The resulting XML files are placed in the connector Output tab.
XML to TRADACOMS
When generating TRADACOMS files, set the Translation Type to XML to TRADACOMS. XML files placed in the Input tab are processed by the connector. The connector converts the XML elements representing a TRADACOMS file into TRADACOMS segments, then uses the configured Transmission Settings to generate the transmission headers. To create an example of the XML structure required to generate TRADACOMS documents, start with an example TRADACOMS document and send it through the TRADACOMS connector in TRADACOMS to XML mode. You can use the resulting XML as a template in the XML Map connector to convert XML structures into TRADACOMS structure.
Use With the XML Map Connector
In accordance with Arc convention, the TRADACOMS connector does one of two things: it receives XML input or generates XML output. To ensure that the input and output files have the correct XML structure, CData strongly recommends that you use the XML Map connector as the previous step in the flow when generating outbound TRADACOMS documents, or as the following step in the flow when receiving inbound TRADACOMS documents. The interaction between the XML Map connector and the TRADACOMS connector is made simple by the Upload Test File feature described below.
Upload Test File
Follow these steps to generate an XML representation of an input file:
- In the Input tab of the connector, click the More dropdown and click Upload Test File.
- Navigate to a file on disk that you want to model as XML, select it, and click OK.
- Connect the TRADACOMS connector to an XML Map connector in the flow. This connection can go in either direction: inbound to the XML Map connector, or outbound from the XML Map connector.
The XML Map connector automatically detects the structure of the test file. Based on where you placed the TRADACOMS connector, the file appears in the Source File or Destination File drop-down menu of the XML Map connector.
Note: XML Map connectors require both a source and destination template, so the remaining template must be set based on the structure the data originates from, or the structure it should be converted to. For example, if the data from the TRADACOMS document needs to be inserted into a database, the other template in the XML Map connector would be the XML model of a database insert. See the XML Map connector’s Using the Mapping Editor for more information on creating the mapping between two template files.
Macros
Using macros in file naming strategies can enhance organizational efficiency and contextual understanding of data. By incorporating macros into filenames, you can dynamically include relevant information such as identifiers, timestamps, and header information, providing valuable context to each file. This helps ensure that filenames reflect details important to your organization.
CData Arc supports these macros, which all use the following syntax: %Macro%.
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
| ConnectorID | Evaluates to the ConnectorID of the connector. |
| Ext | Evaluates to the file extension of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| Filename | Evaluates to the filename (extension included) of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| FilenameNoExt | Evaluates to the filename (without the extension) of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| MessageId | Evaluates to the MessageId of the message being output by the connector. |
| RegexFilename:pattern | Applies a RegEx pattern to the filename of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| Header:headername | Evaluates to the value of a targeted header (headername) on the current message being processed by the connector. |
| LongDate | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in long-handed format (for example, Wednesday, January 24, 2024). |
| ShortDate | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in a yyyy-MM-dd format (for example, 2024-01-24). |
| DateFormat:format | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in the specified format (format). See Sample Date Formats for the available datetime formats |
| Vault:vaultitem | Evaluates to the value of the specified vault item. |
Examples
Some macros, such as %Ext% and %ShortDate%, do not require an argument, but others do. All macros that take an argument use the following syntax: %Macro:argument%
Here are some examples of the macros that take an argument:
- %Header:headername%: Where
headernameis the name of a header on a message. - %Header:mycustomheader% resolves to the value of the
mycustomheaderheader set on the input message. - %Header:ponum% resolves to the value of the
ponumheader set on the input message. - %RegexFilename:pattern%: Where
patternis a regex pattern. For example,%RegexFilename:^([\w][A-Za-z]+)%matches and resolves to the first word in the filename and is case insensitive (test_file.xmlresolves totest). - %Vault:vaultitem%: Where
vaultitemis the name of an item in the vault. For example,%Vault:companyname%resolves to the value of thecompanynameitem stored in the vault. - %DateFormat:format%: Where
formatis an accepted date format (see Sample Date Formats for details). For example,%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff%resolves to the date and timestamp on the file.
You can also create more sophisticated macros, as shown in the following examples:
- Combining multiple macros in one filename:
%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff%%EXT% - Including text outside of the macro:
MyFile_%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff% - Including text within the macro:
%DateFormat:'DateProcessed-'yyyy-MM-dd_'TimeProcessed-'HH-mm-ss%