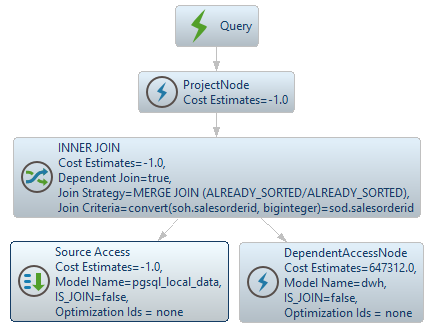
複数の Data Sources にまたがる大小のテーブルを結合する場合。Dependent Joinは、大きなテーブルから返される行の量を減らすのに最適な方法です。以下のクエリを考えてみましょう:
SELECT soh.customerid, soh.subtotalFROM dwh.SalesOrderDetailBig sod JOIN pgsql_local_data.SalesOrderHeader soh ON sod.salesorderid = soh.salesorderid OPTION MAKEDEP dwh.SalesOrderDetailBig;;CCData Virtuality Server はまず、小さいテーブルから 行を取得します:
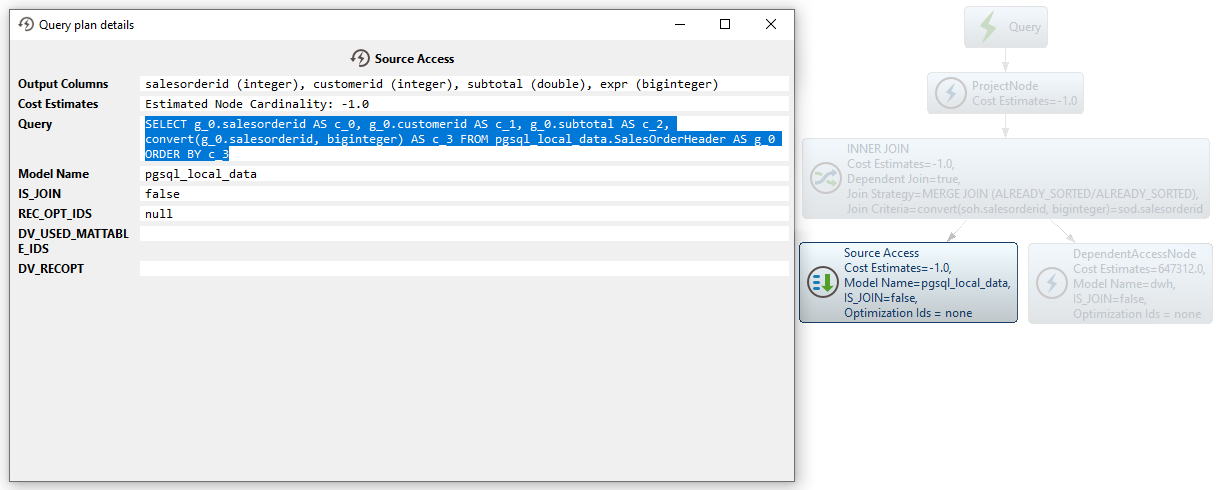
SELECT g_0.salesorderid AS c_0, g_0.customerid AS c_1, g_0.subtotal AS c_2, convert(g_0.salesorderid, biginteger) AS c_3 FROM pgsql_local_data.SalesOrderHeader AS g_0 ORDER BY c_3次に、小さいテーブルからのsalesorderid値が、大きいテーブルからのデータを制限するWHERE IN句を生成するために使用されます。これにより、クエリ処理に必要なメモリとCPUの使用量を大幅に削減することができます(アイコンに注目):
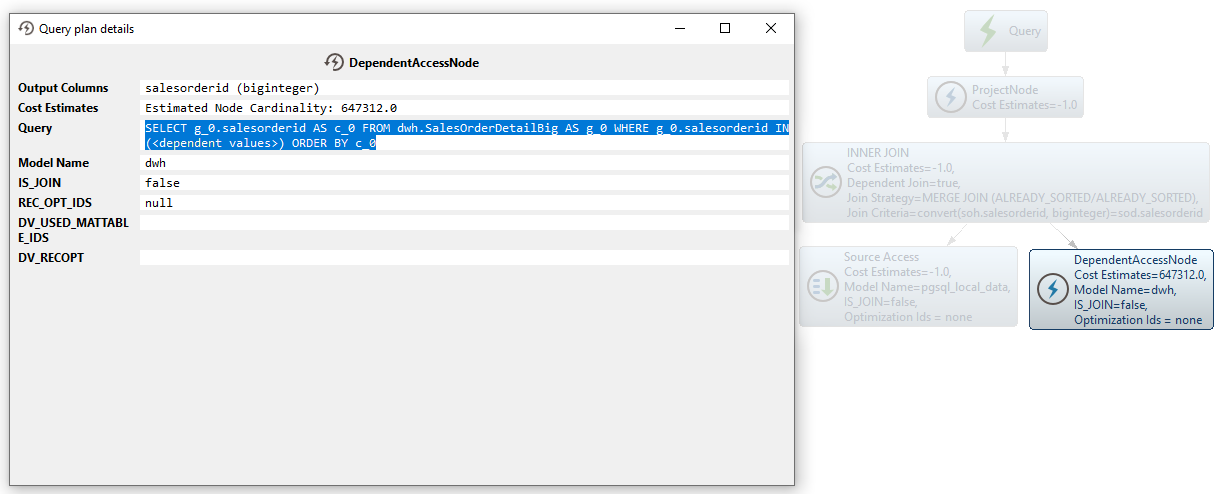
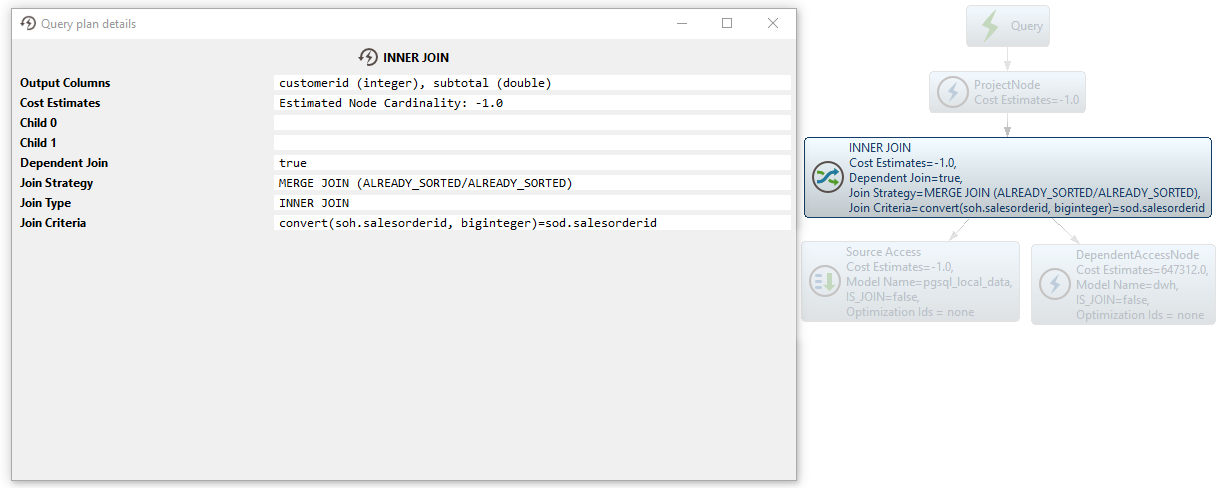
SELECT g_0.salesorderid AS c_0 FROM dwh.SalesOrderDetailBig AS g_0 WHERE g_0.salesorderid IN (<dependent values>) ORDER BY c_0その後、Merge Joinが実行され、両方の結果セットが結合されます:
While for large tables the benefits of splitting a query into multiple ones and executing it on one of the sources seem straightforward, for smaller tables, the costs of running multiple queries can be higher than the effects of the parallelism. The exact tradeoff is hard to predict automatically. Because of this, we recommend using dependent joins sparingly and, as discussed in a later chapter, only gathering data source statistics in case some very large tables are present in the joins. A Merge Join is almost always preferable to Dependent Join for smaller tables.