Creating a Service Principal App in Entra ID (Azure AD)
Creating a Service Principal App in Entra ID (Azure AD)
Note: Microsoft has rebranded Azure AD as Entra ID. In topics that require the user to interact with the Entra ID Admin site, we use the same names Microsoft does. However, there are still CData connection properties whose names or values reference "Azure AD".
PostgreSQL supports Service Principal-based authentication, which is role-based. This means that the Service Principal's permissions are determined by the roles assigned to it. The roles specify what resources the Service Principal can access and which operations it can perform.
If you want to use a Service Principal to authenticate to PostgreSQL, you must create a custom application in Microsoft Entra ID.
To enable Service Principal authentication:
- Confirm that you have permission to register applications and assign roles in your tenant.
- Register a new application and configure credentials and permissions in the Entra Admin Center.
Registering the Application
- Go to https://portal.azure.com.
- In the left-hand navigation pane, select Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations.
- Click New registration.
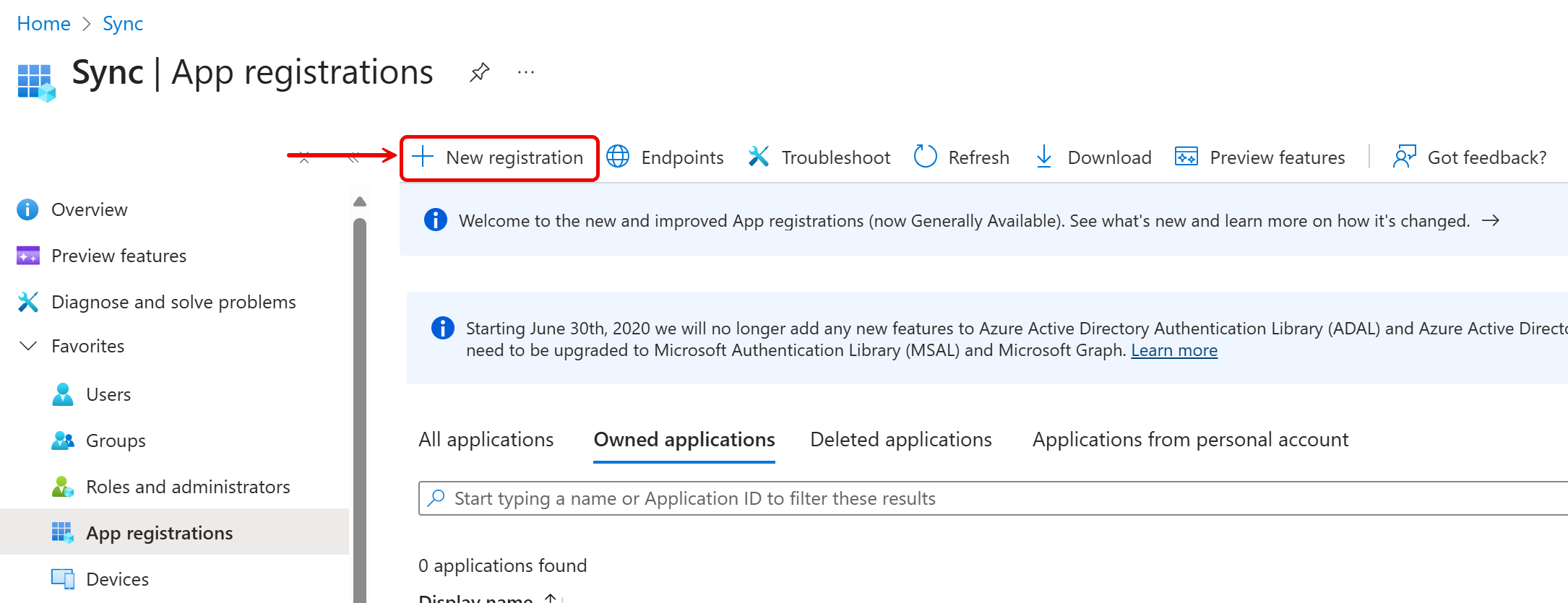
- Enter a name for the application.
- Select the desired tenant setup. Since this custom application is for Service Principal use, choose Any Microsoft Entra ID tenant – Multitenant.
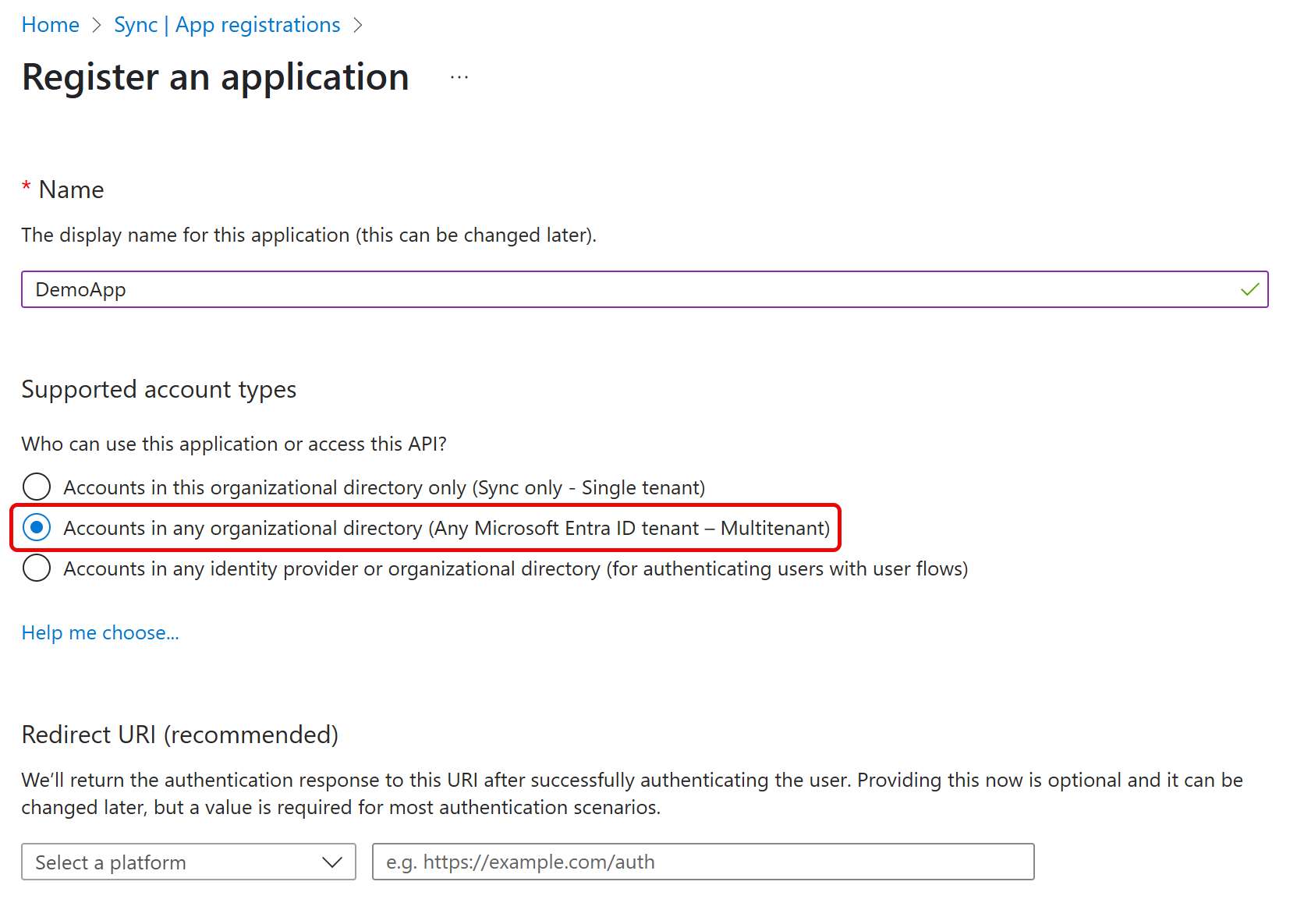
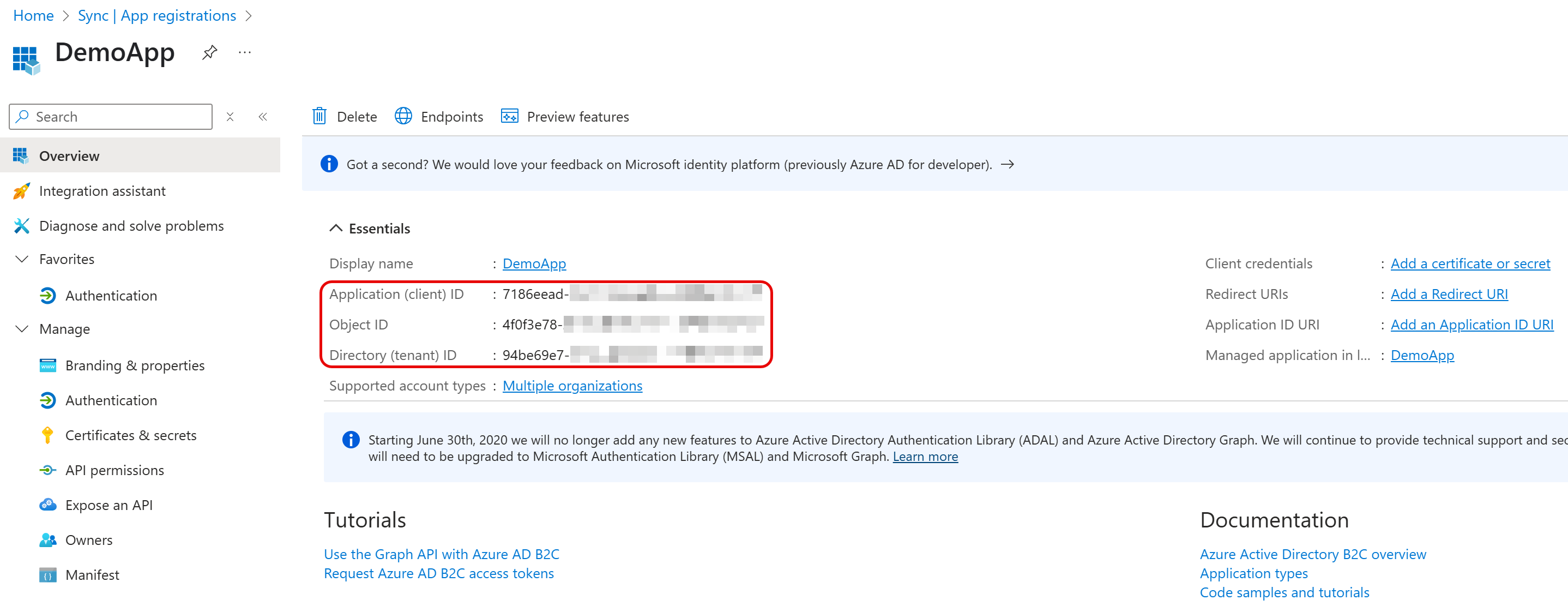
- Click Register. The application management screen opens. Note the value in Application (client) ID as the OAuthClientId and the Directory (tenant) ID as the AzureTenant
- If authenticating with a user context, select Azure OSSRDBMS Database -> Delegated Permissions -> user_impersonation. When authenticating without a user context, select Azure OSSRDBMS Database -> Application Permissions -> app_impersonation.
- Navigate to Certificates & Secrets and define the application authentication type. Two types of authentication are available: certificate (recommended) or client secret
- For certificate authentication: In Certificates & Secrets, select Upload certificate, then upload the certificate from your local machine. For more information on creating a self-signed certificate, see Create a self-signed certificate
- For creating a new client secret: In Certificates & Secrets, select New Client Secret for the application and specify its duration. After the client secret is saved, PostgreSQL displays the key value. This value is displayed only once, so be sure to record it for future use. Use this value for the OAuthClientSecret
- Navigate to Authentication and select the Access tokens option.
- Save your changes.
- If you specified permissions that require admin consent (such as the Application Permissions), you can grant them from the current tenant on the API Permissions page.
Granting Admin Consent
Some custom applications require administrative permissions to operate within a Microsoft Entra ID tenant. This is especially true for applications that use Application permissions, which allow the app to run without a signed-in user. Admin consent can be granted when creating a new application, by adding relevant permissions marked as "Admin Consent Required". Admin consent is also required to use Client Credentials in the authentication flow.These permissions must be granted by an admin. To grant admin consent:
- Log in to https://portal.azure.com with an administrator account.
- Navigate to Microsoft Entra ID > App registrations and select your registered application.
- Navigate to API permissions.
- Review the permissions listed under Application permissions. Ensure the necessary API scopes are included for your use case.
- Click Grant admin consent to approve the requested permissions.
Consent for Client Credentials
OAuth supports the use of client credentials to authenticate. In a client credentials authentication flow, credentials are created for the authenticating application itself. The authentication flow acts just like the usual auth flow, except that there is no prompt for an associated user to provide credentials. All tasks accepted by the application are executed outside of the context of a default user.Note: Since the embedded OAuth credentials authenticate on a per-user basis, you cannot use them in a client authentication flow. You must always create a custom OAuth application to use client credentials.
- Log in to https://portal.azure.com
- Create a custom OAuth application, as described above.
- Navigate to App Registrations.
- Find the application you just created, and open API Permissions.
- Select the Microsoft Graph permissions. There are two distinct sets of permissions: Delegated and Application.
- For use with Service Principal, specify Application permissions.
- Select any additional permissions you require for your integration.