IBM MQ Connector
Version 23.4.8841
Version 23.4.8841
IBM MQ Connector
The IBM MQ connector provides access to IBM MQ queues through the REST API.
Overview
IBM MQ connectors are configured with a specific queue to which messages are pushed or from which messages are retrieved. Files that arrive in the Input tab of the connector are pushed as a message to the queue, and messages pulled from the queue are written as files to the Output tab. Each connector instance can only be configured with a single queue.
Connector Configuration
This section contains all of the configurable connector properties.
Settings Tab
Configuration
Settings related to the core configuration of the connector.
- Connector Id The static, unique identifier for the connector.
- Connector Type Displays the connector name and a description of what it does.
- Connector Description An optional field to provide a free-form description of the connector and its role in the flow.
- Remote Host The hostname or IP address of the system hosting the MQ service.
- Remote Port The port on the remote host where the MQ service is listening.
- Queue Manager The name of the local queue manager for the desired queue.
- Queue The name of the queue to push messages to or pull messages from.
TLS Settings
Settings related to transport security.
- Use TLS when connecting with IBM MQ servers Whether to use TLS encryption as transport security when connecting and communicating with IBM MQ servers. When disabled, all communication is in plain text.
- Server Public Certificate When TLS is enabled, set this field to the TLS/SSL certificate that the IBM MQ presents to verify its identity. Set this to Any Certificate to implicitly trust the IBM MQ server.
Client Authentication
Settings related to authenticating against the remote service.
- Username The username credential for authenticating against the remote server.
- Password The password for the specified username.
Other Settings
Settings not included in the previous categories.
- Local File Scheme A scheme for assigning filenames to messages that are output by the connector. You can use macros in your filenames dynamically to include information such as identifiers and timestamps. For more information, see Macros.
Message
- Save to Sent Folder Check this to copy files processed by the connector to the Sent folder for the connector.
- Sent Folder Scheme Instructs the connector to group messages in the Sent folder according to the selected interval. For example, the Weekly option instructs the connector to create a new subfolder each week and store all messages for the week in that folder. The blank setting tells the connector to save all messages directly in the Sent folder. For connectors that process many messages, using subfolders helps keep messsages organized and improves performance.
Logging
- Log Level The verbosity of logs generated by the connector. When you request support, set this to Debug.
- Log Subfolder Scheme Instructs the connector to group files in the Logs folder according to the selected interval. For example, the Weekly option instructs the connector to create a new subfolder each week and store all logs for the week in that folder. The blank setting tells the connector to save all logs directly in the Logs folder. For connectors that process many transactions, using subfolders helps keep logs organized and improves performance.
- Log Messages Check this to have the log entry for a processed file include a copy of the file itself. If you disable this, you might not be able to download a copy of the file from the Input or Output tabs.
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous settings are for specific use cases.
- Other Settings Enables you to configure hidden connector settings in a semicolon-separated list (for example,
setting1=value1;setting2=value2). Normal connector use cases and functionality should not require the use of these settings.
Automation Tab
Automation Settings
Settings related to the automatic processing of files by the connector.
- Send Whether files arriving at the connector are automatically sent.
- Retry Interval The number of minutes before a failed send is retried.
- Max Attempts The maximum number of times the connector processes the file. Success is measured based on a successful server acknowledgement. If you set this to 0, the connector retries the file indefinitely.
- Receive Whether the connector should automatically query the data source.
- Receive Interval The interval between automatic query attempts.
- Minutes Past the Hour The minutes offset for an hourly schedule. Only applicable when the interval setting above is set to Hourly. For example, if this value is set to 5, the automation service downloads at 1:05, 2:05, 3:05, etc.
- Time The time of day that the attempt should occur. Only applicable when the interval setting above is set to Daily, Weekly, or Monthly.
- Day The day on which the attempt should occur. Only applicable when the interval setting above is set to Weekly or Monthly.
- Minutes The number of minutes to wait before attempting the download. Only applicable when the interval setting above is set to Minute.
- Cron Expression A five-position string representing a cron expression that determines when the attempt should occur. Only applicable when the interval setting above is set to Advanced.
Performance
Settings related to the allocation of resources to the connector.
- Max Workers The maximum number of worker threads consumed from the threadpool to process files on this connector. If set, this overrides the default setting on the Settings > Automation page.
- Max Files The maximum number of files sent by each thread assigned to the connector. If set, this overrides the default setting on the Settings > Automation page.
アラートタブ
アラートとサービスレベル(SLA)の設定に関連する設定.
コネクタのE メール設定
サービスレベル(SLA)を実行する前に、通知用のE メールアラートを設定する必要があります。アラートを設定をクリックすると、新しいブラウザウィンドウで設定ページが開き、システム全体のアラートを設定することができます。詳しくは、アラートを参照してください。
サービスレベル(SLA)の設定
サービスレベルでは、フロー内のコネクタが送受信すると予想される処理量を設定し、その量が満たされると予想される時間枠を設定できます。CData Arc は、サービスレベルが満たされていない場合にユーザーに警告するE メールを送信し、SLA を At Risk(危険) としてマークします。これは、サービスレベルがすぐに満たされない場合に Violated(違反) としてマークされることを意味します。これにより、ユーザーはサービスレベルが満たされていない理由を特定し、適切な措置を講じることができます。At Risk の期間内にサービスレベルが満たされなかった場合、SLA はViolated としてマークされ、ユーザーに再度通知されます。
サービスレベルを定義するには、予想処理量の条件を追加をクリックします。
- コネクタに個別の送信アクションと受信アクションがある場合は、ラジオボタンを使用してSLA に関連する方向を指定します。
- 検知基準(最小)を、処理が予想されるトランザクションの最小値(量)に設定し、毎フィールドを使用して期間を指定します。
- デフォルトでは、SLA は毎日有効です。これを変更するには、毎日のチェックをOFF にし、希望する曜日のチェックをON にします。
- 期間終了前にステータスを’At Risk’ に設定するタイミングを使用して、SLA がAt Risk としてマークされるようにします。
- デフォルトでは、通知はSLA が違反のステータスになるまで送信されません。これを変更するには、‘At Risk’ 通知を送信のチェックをON にします。
次の例は、月曜日から金曜日まで毎日1000ファイルを受信すると予想されるコネクタに対して構成されたSLA を示しています。1000ファイルが受信されていない場合、期間終了の1時間前にAt Risk 通知が送信されます。
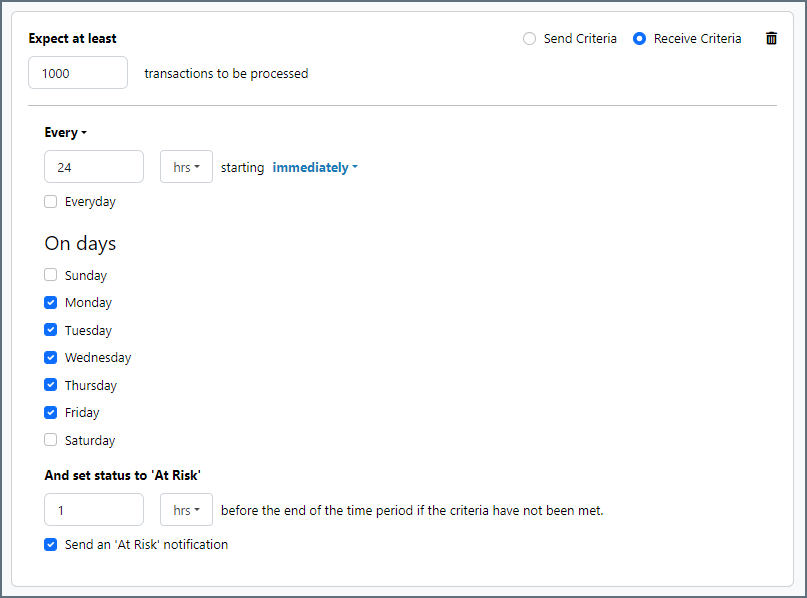
Establishing a Connection
The following settings are required to establish a connection:
- Remote Host
- Remote Port
- Queue Manager
- Queue
If client authentication is required, you must also set the following:
- Username
- Password
Use the Test Connection button to verify the connection to the server.
Sending Messages
Files that arrive in the Input tab for the connector are pushed to the configured queue as a message. Files can arrive in this folder either by being placed there directly, or from another connector earlier in the flow.
You need to set up multiple IBM MQ connectors to push messages to multiple queues. You can use a connector like the Branch connector to route files to the appropriate IBM MQ connector.
Receiving Messages
You can configure the IBM MQ connector to automatically poll the remote queue for messages to download. Use the Receive Automation and Receive Interval settings on the Automation tab. When enabled, the connector waits for the specified interval before attempting to retrieve messages from the queue and pushing them to the Output folder.
If the IBM MQ connector is connected to other connectors in a flow, downloaded messages are automatically passed to the next connector. Otherwise, the messages remain in the Output folder.
Macros
Using macros in file naming strategies can enhance organizational efficiency and contextual understanding of data. By incorporating macros into filenames, you can dynamically include relevant information such as identifiers, timestamps, and header information, providing valuable context to each file. This helps ensure that filenames reflect details important to your organization.
CData Arc supports these macros, which all use the following syntax: %Macro%.
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
| ConnectorID | Evaluates to the ConnectorID of the connector. |
| Ext | Evaluates to the file extension of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| Filename | Evaluates to the filename (extension included) of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| FilenameNoExt | Evaluates to the filename (without the extension) of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| MessageId | Evaluates to the MessageId of the message being output by the connector. |
| RegexFilename:pattern | Applies a RegEx pattern to the filename of the file currently being processed by the connector. |
| Header:headername | Evaluates to the value of a targeted header (headername) on the current message being processed by the connector. |
| LongDate | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in long-handed format (for example, Wednesday, January 24, 2024). |
| ShortDate | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in a yyyy-MM-dd format (for example, 2024-01-24). |
| DateFormat:format | Evaluates to the current datetime of the system in the specified format (format). See サンプル日付フォーマット for the available datetime formats |
| Vault:vaultitem | Evaluates to the value of the specified vault item. |
Examples
Some macros, such as %Ext% and %ShortDate%, do not require an argument, but others do. All macros that take an argument use the following syntax: %Macro:argument%
Here are some examples of the macros that take an argument:
- %Header:headername%: Where
headernameis the name of a header on a message. - %Header:mycustomheader% resolves to the value of the
mycustomheaderheader set on the input message. - %Header:ponum% resolves to the value of the
ponumheader set on the input message. - %RegexFilename:pattern%: Where
patternis a regex pattern. For example,%RegexFilename:^([\w][A-Za-z]+)%matches and resolves to the first word in the filename and is case insensitive (test_file.xmlresolves totest). - %Vault:vaultitem%: Where
vaultitemis the name of an item in the vault. For example,%Vault:companyname%resolves to the value of thecompanynameitem stored in the vault. - %DateFormat:format%: Where
formatis an accepted date format (see サンプル日付フォーマット for details). For example,%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff%resolves to the date and timestamp on the file.
You can also create more sophisticated macros, as shown in the following examples:
- Combining multiple macros in one filename:
%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff%%EXT% - Including text outside of the macro:
MyFile_%DateFormat:yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss-fff% - Including text within the macro:
%DateFormat:'DateProcessed-'yyyy-MM-dd_'TimeProcessed-'HH-mm-ss%